
-

MENU
- Home
- Osteopathy
- Effects of Osteopathy
- Fees
- Consultation
- Profile
- Access・Contact
LANGUAGE
No medical prescription is necessary; osteopathy is a first-line treatment A consultation lasts about 60 minutes. Osteopathy is a manual therapy; therefore the therapist utilizes only her hands for examination and treatment.
The consultation procedure in several steps :
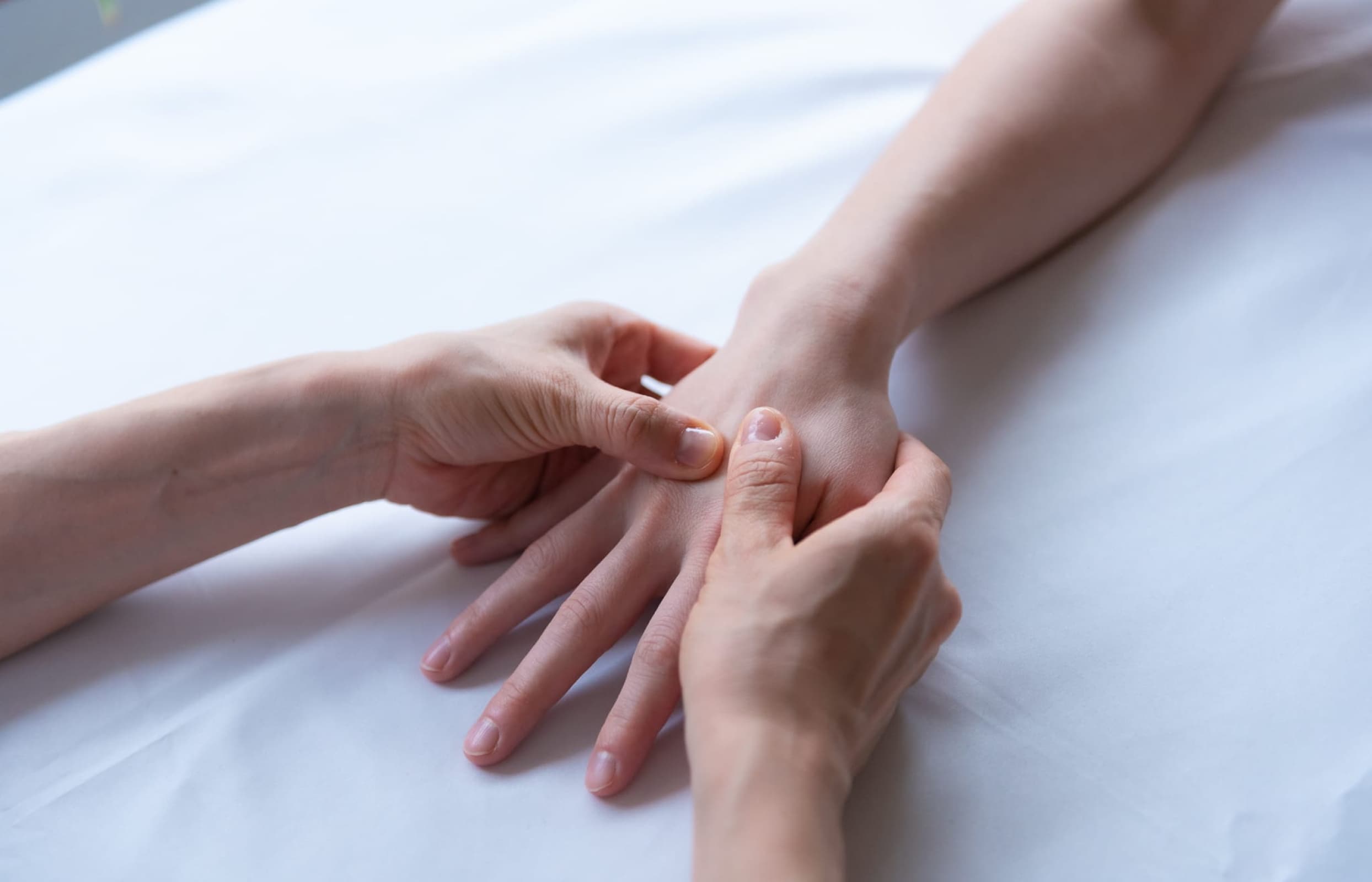

The consultation begins with anamnesis, an exploratory discussion allowing the patient to reveal their concerns and motives for consulting
Initially, the osteopath will conduct tests to verify if treatment of the problem is within their realm.
Various osteopathic examinations will follow on different parts of the body.
The goal of these examinations is to determine whether the imbalance of the totality of systems that composes the body originated due to modifications to tissue quality or mobility restrictions.
As a result of this global osteopathic approach the therapist can compose a treatment utilizing specific techniques adapted to each patient.
When necessary, the osteopath will propose simple, daily stretching or exercises. The goal of these exercises is to maintain and stabilize the organism’s new equilibrium.
It is important to be aware that symptoms are not treated directly, instead the osteopath aims to reestablish structural and functional integrity restoring a homeostasis* unique to each patient.
*Homeostasis: the mechanism that enables the organism to maintain physiological equilibrium
As long as the relationship structures-functions remains balanced, the body can surmount suffering through its natural capacity for healing and self-regulation.
The body requires time to adapt to this new equilibrium as the physical components begin to function again harmoniously.
Once the organism finds this stable balance, ‟nature” finishes the job.
In most cases, this is the reason why problems will begin to dissipate after a single session or within days following treatment.
Improvement of symptoms will also depend on particular cases and the physical, psychological, or environmental conditions of each patient. Treatment might require one, several, or periodic consultations spread over a period of time.
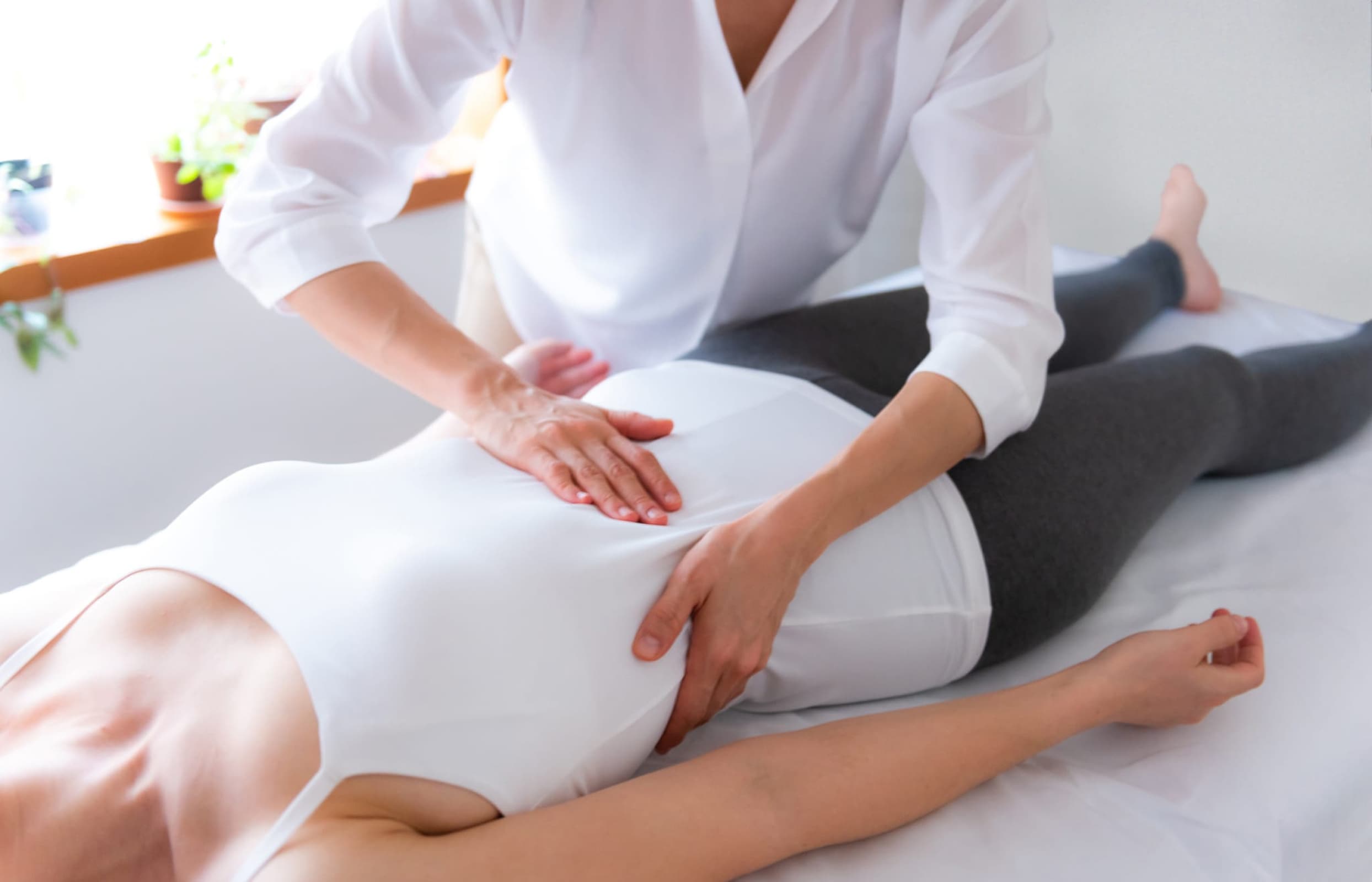

In order to tailor an approach for each individual, we combine different techniques.
Restoring joint mobility by working on the neurological reflex. Generally, a small crack might be heard during a manipulation.
The noise is caused by a release of gas from the joint capsule: this is not the sound of bone cracking. Osteopaths never force beyond a joint’s physiological limits.
Restoring joint mobility through muscular contractions and the neuromuscular reflex.
Restoring joint mobility through muscular contractions and the neuromuscular reflex.
Relieving muscular pain and releasing restrictions in joints through vibration, pressure, stretching, etc.
Recuperation of joint mobility improves blood flow, lymphatic activity, encouraging better drainage and nourishment of the joints and surrounding areas.
All the viscera/organs are implicated. Precise attention to re-energize and revitalize each organ to promote proper function.
Liberate myofascial tension (the fascia, composed of conjunctive tissue, is like a membrane enveloping the entire body.)
Freeing tension or emotions/stress blocked in the tissue. Favor local and global body functions. Regain joint and tissue mobility.
Encourage tissue health and vitality. *Tissue: a group of cells
Working on the bone itself and the sutures (where skull bones join to together), membranes and cranial vessels, or cranial mobility.
Rebalance and reharmonize the various functions of the entire body.
Working on the dura mater (a layer of the meninges). Rebalance and revitalize various functions of the entire body. Encourage spinal column mobility.